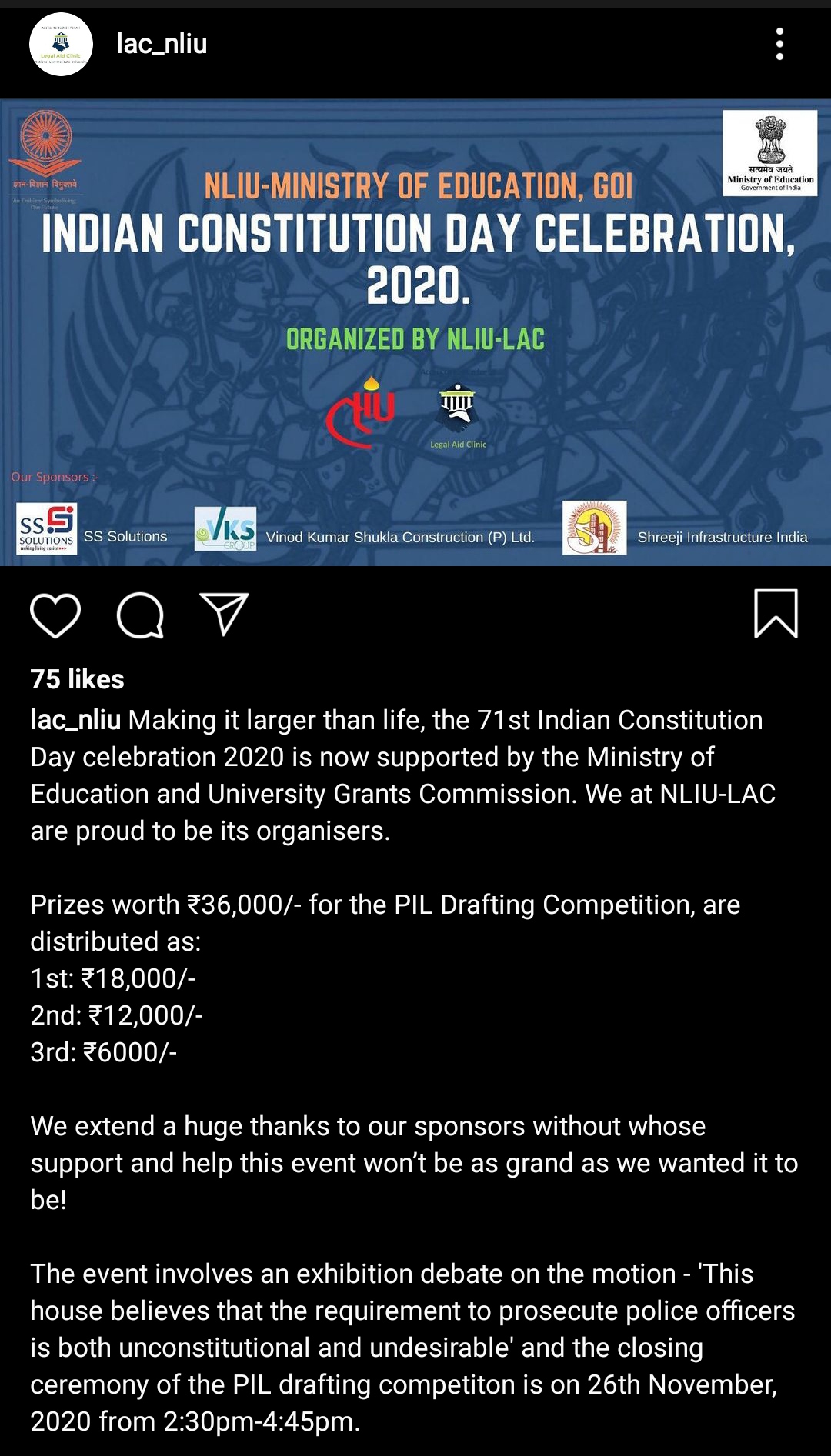
The following is a table listing granting and withdrawing of their ‘General Consent’ Granted To CBI To Investigate Cases In The State.
Some State governments innocently think by withdrawing ‘General Consent’ Granted To CBI To Investigate Cases In The State, they can stop CBI. Fools !!! Here why.
| State / Union Territory |
Consent Granted on |
Consent Withdrawn on |
| Andhra Pradesh |
3 Aug 2018
6 Jun 2019 |
16 Nov 2018 (Confidential GO)
— |
| Arunachal Pradesh |
|
|
| Assam |
|
|
| Bihar |
|
|
| Chhattisgarh |
2001 |
10 Jan 2019 |
| Goa |
|
|
| Gujarat |
|
|
| Haryana |
|
|
| Himachal Pradesh |
|
|
| Jharkhand |
|
5 Nov 2020
|
| Karnataka |
|
|
| Kerala |
|
4 Nov 2020 |
| Madhya Pradesh |
|
|
| Maharashtra |
|
21 Oct 2020 |
| Manipur |
|
|
| Meghalaya |
|
|
| Mizoram |
|
|
| Nagaland |
|
|
| Odisha |
|
|
| Punjab |
|
6 Nov 2020 |
| Rajasthan |
|
19 Sep 2020 |
| Sikkim |
|
|
| Tamil Nadu |
|
|
| Telangana |
|
|
| Tripura |
|
|
| Uttar Pradesh |
|
|
| Uttarakhand |
|
|
| West Bengal |
|
|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
|
|
| Chandigarh |
|
|
| Dadra Nagar Haveli and Daman Diu |
|
|
| Delhi |
|
|
| Jammu and Kashmir |
|
|
| Ladakh |
|
|
| Lakshadweep |
|
|
| Puducherry |
|
|
On 6 Jun 2019, Andhra Pradesh granted General Consent.
03082018HO_MS109
*****
On 16 Nov 2018, Andhra Pradesh withdrew General Consent.
(Via Confidential GO and a Gazette notification)
2018-11-20 Withdrawal of General consent given to the members of CBI Gaz
*****
On 3 Aug 2018, Andhra Pradesh granted General Consent.
2018-08-03 03082018HO_MS109 General consent given to the members of CBI
*****
On 5 Dec 2017, Andhra Pradesh granted General Consent.
2017-12-05 2017HO_MS184 General consent given to the members of CBI
On 10 Jan 2019, Chattisgarh withdrew General Consent.
2019-01-10 Chattishgarh withdraws General Consent
On 5 Nov 2020, Jharkhand withdrew General Consent.
Jharkhand withdraws General Consent
On 4 Nov 2020, Kerala withdrew General Consent.
2020-11-04 Kerala withdraws General Consent
On 21 Oct 2020, Maharashtra withdrew General Consent.
2020-10-21 Maharashtra withdraws General Consent
On 19 Sep 2020, Rajasthan withdrew General Consent.
2020-07-19 Rajasthan withdraws General Consent
On 6 Nov 2020, Punjab withdrew General Consent.
Final_Gazette_Report